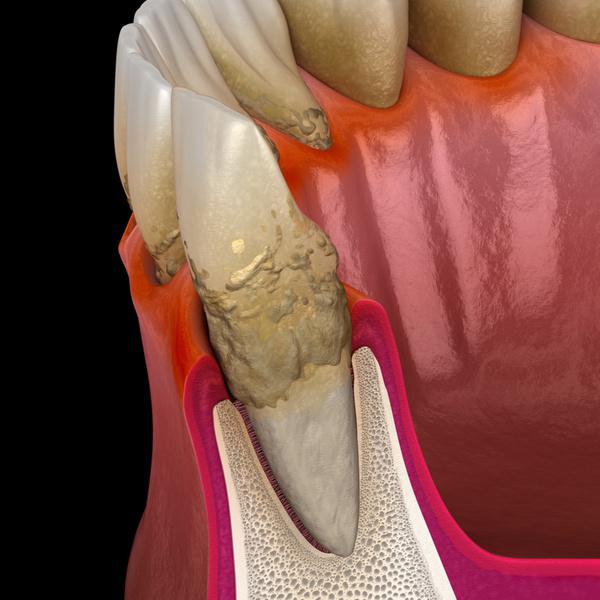
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, develops when plaque and bacteria accumulate between the teeth and gums. If not managed, this buildup leads to gum infection and, as the condition worsens, treatment becomes more difficult and uncomfortable. Advanced gum disease can result in tooth loss.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Symptoms vary depending on how far the disease has progressed and may include:
- Swollen or tender gums
- Red, inflamed gums
- Gums that bleed easily
- Gum recession
- Loose teeth
- Persistent bad breath
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
Causes and Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease is primarily caused by plaque, a film of bacteria that forms on teeth after eating. If not removed through regular brushing, plaque irritates the gums and can progress through two main stages:
Gingivitis
This is the earliest stage. Gums become red, swollen, and may bleed easily. Gingivitis is generally mild and can be reversed with professional dental cleaning and good oral hygiene habits at home.
Periodontitis
If untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis—a more severe form of gum disease. At this stage, the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets where bacteria collect. Bone and connective tissue supporting the teeth start to break down, which may lead to tooth loosening or loss.
Treatment of Gum Disease
Treating gum disease typically involves a periodontist and depends on how advanced the disease is. Common treatment options include:
Scaling and Root Planing
A deep-cleaning procedure that removes plaque and bacteria from below the gumline and along the tooth roots, helping the gums reattach to clean surfaces.
Medications
Antibiotics or antimicrobial agents may be prescribed to fight infection and reduce the size of gum pockets, promoting healing and reducing inflammation.
Surgical Treatments
If non-surgical therapies are unsuccessful, surgical interventions such as flap surgery may be needed to access and clean deep gum pockets. Gum or bone grafts can help rebuild areas damaged by periodontitis.
Prevention of Gum Disease
Most gum disease is preventable with good dental care. Key recommendations include:
- Brush and floss daily
- Avoid tobacco use
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Visit your dentist regularly for exams and cleanings
Prompt dental care is essential if you notice any signs of gum disease. Early intervention can prevent more serious complications and protect your oral health.
Book Online
Elevate Your Dental Experience
Our team at Pristine Smiles is ready to help you care for your smile. Count on our dedicated team for quality dental care in a comfortable environment. Schedule your appointment today!

